Understanding the Role of Lamina in Football Player Performance
October 17, 2024As a professional footballer operating at the highest level, I’m acutely aware of the critical role physical conditioning plays in achieving peak performance. Every aspect of our training is meticulously designed to optimize strength, speed, agility, and endurance. One crucial element often overlooked in discussions about player fitness is the role of lamina. In this article, we’ll delve into the importance of lamina, its impact on a footballer’s ability, and how to maintain its health for a long and successful career.
What is Lamina and Why is it Important for Footballers?
Lamina, in the context of human anatomy, refers to the vertebral lamina, a bony plate that forms the posterior part of each vertebra, protecting the spinal cord. For footballers constantly jumping, twisting, tackling, and absorbing impact, a strong and healthy spine is non-negotiable.
 Football Player Executing a Tackle
Football Player Executing a Tackle
Here’s why lamina health is paramount for footballers:
- Spinal Stability and Flexibility: The lamina provides essential structural support to the spine, allowing for a wide range of movement – bending, twisting, extending – crucial for a footballer’s agility and ball control.
- Protection of the Spinal Cord: The spinal cord, responsible for transmitting nerve impulses throughout the body, is housed within the vertebral column formed by the lamina. Any damage to the lamina can have severe consequences, affecting movement and even leading to paralysis.
- Shock Absorption: During high-impact activities like running, jumping, and landing, the lamina helps to distribute and absorb shock, protecting the vertebrae and intervertebral discs from injury.
Common Lamina-Related Issues in Football
Football, despite its excitement and rewards, places immense physical demands on players, making them susceptible to various lamina-related problems. These can include:
- Stress Fractures: Repetitive stress from constant running and impact can lead to tiny cracks in the lamina, causing pain and hindering performance.
- Spondylolysis: A more serious condition, spondylolysis involves a defect or fracture in the pars interarticularis, a small, thin bone connecting two parts of the vertebra.
- Spondylolisthesis: This occurs when a vertebra, weakened by a stress fracture or defect, slips forward over the one below it, leading to instability and pain.
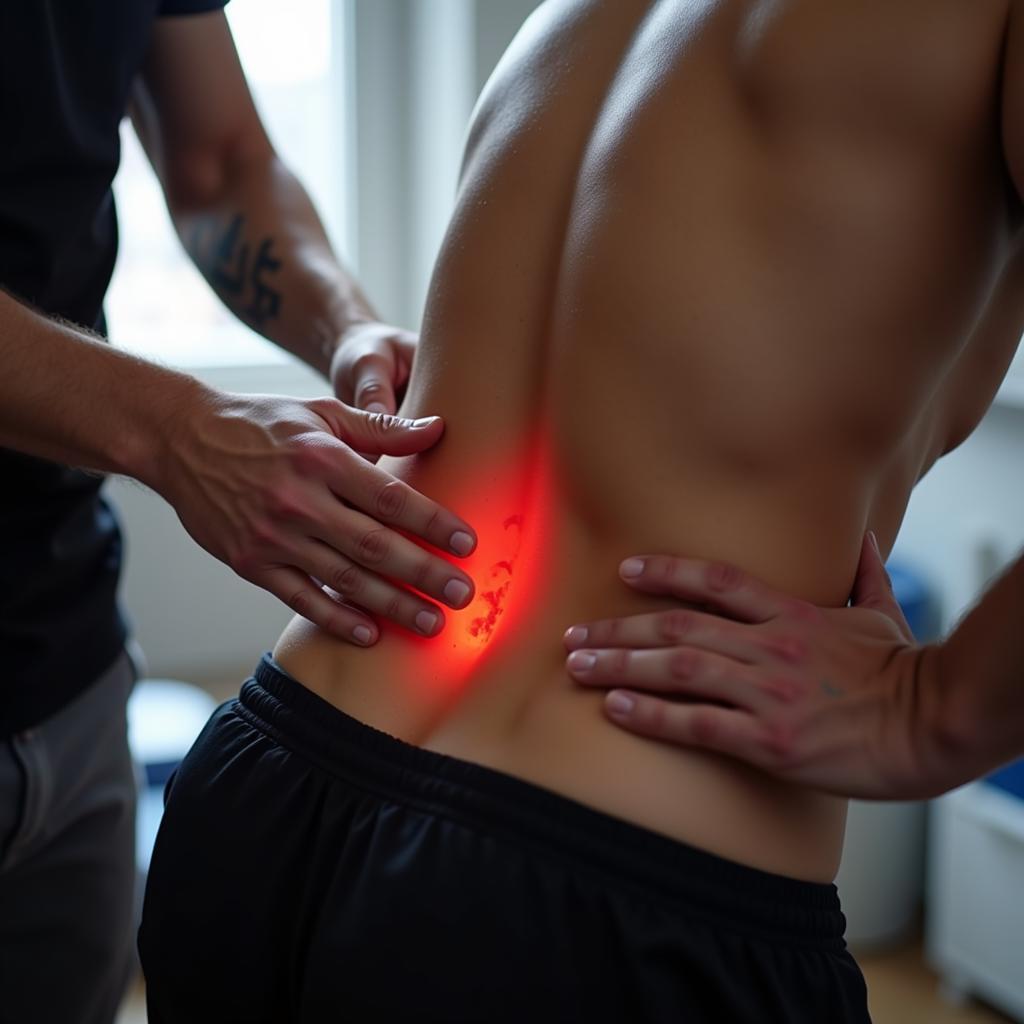 Footballer Receiving Physiotherapy Treatment
Footballer Receiving Physiotherapy Treatment
Maintaining Lamina Health: Tips for Footballers
Maintaining optimal lamina health is crucial not only for maximizing on-field performance but also for ensuring a long and injury-free career. Here are some key tips:
- Core Strengthening: A strong core is essential for supporting the spine and reducing the risk of lamina injuries. Include exercises that target the abdominal and back muscles in your training regimen.
- Proper Warm-up and Cool-down: Never underestimate the importance of adequately warming up before training or matches and cooling down afterward. This helps prepare your muscles and joints, including your spine, for the stresses of exercise and aids in recovery.
- Correct Technique: Ensure you’re using proper techniques for all exercises and movements on the field, especially when lifting weights or engaging in high-impact activities. This helps to distribute force evenly and minimizes strain on the spine.
- Adequate Rest and Recovery: Give your body sufficient time to rest and recover after training and matches. This allows your muscles and bones, including the lamina, to repair and rebuild.
- Nutrition and Hydration: Maintain a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, essential for bone health. Stay adequately hydrated, which is crucial for overall physical function and injury prevention.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular check-ups with your physician or physiotherapist can help identify and address any potential issues early on before they escalate into more serious problems.
Conclusion
As an athlete who pushes physical limits, I understand the critical importance of lamina health for any footballer. By incorporating the tips outlined above and working closely with your medical team, you can ensure your spine remains strong and resilient, allowing you to perform at your best and enjoy a long and successful career on the pitch.
FAQ
1. What are the symptoms of a lamina injury?
Symptoms can vary depending on the severity but often include lower back pain, stiffness, muscle spasms, pain that radiates down the legs, numbness or tingling in the extremities, and weakness in the legs.
2. How are lamina injuries diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, reviewing your medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to visualize the spine and identify any abnormalities.
3. Can lamina injuries heal on their own?
Minor stress fractures can often heal with conservative treatment, including rest, medication, physical therapy, and bracing. However, more severe cases, such as spondylolisthesis, may require surgical intervention.
4. What are the long-term effects of lamina injuries?
Untreated lamina injuries can lead to chronic pain, limited mobility, spinal instability, and an increased risk of developing arthritis or other degenerative spinal conditions later in life.
5. How can I prevent lamina injuries?
Focus on maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise that strengthens the core and back muscles, using proper lifting techniques, avoiding repetitive stress on the spine, and seeking prompt medical attention for any back pain or discomfort.
6. What type of doctor should I see for a lamina injury?
You can consult with your primary care physician, an orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine surgery, or a physiatrist (physical medicine and rehabilitation doctor).
7. What is the recovery time for a lamina injury?
Recovery time varies greatly depending on the severity of the injury, the chosen treatment method, and individual healing rates. It can range from a few weeks for minor stress fractures to several months or longer for surgical cases.
Need More Information?
For further inquiries regarding lamina health or other football-related topics, please refer to our other informative articles on this website.
Get in Touch!
If you have any questions or need assistance, please don’t hesitate to contact us!
- Phone: 0396443476
- Email: [email protected]
- Address: 23 Tháng 3, Đắk Nia, Gia Nghĩa, Đắk Nông, Việt Nam
We have a dedicated customer support team available 24/7 to help you.