How to File an Application for Enforcement of an Award
October 18, 2024Filing an application for the enforcement of an award is a crucial step in ensuring that a successful legal claim translates into tangible results. Whether you’re a triumphant party in an arbitration proceeding or the holder of an unsatisfied judgment, understanding the enforcement process is key to securing the compensation you deserve. This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough of how to file an application for enforcement, demystifying the procedures and empowering you to navigate the legal landscape confidently.
Understanding the Enforcement Process
The enforcement of an award, be it an arbitral award or a court judgment, is the process of compelling the losing party to fulfill its obligations as determined by a neutral decision-making body. This process can vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the award itself.
Types of Awards
There are primarily two types of awards that are commonly enforced:
- Arbitral Awards: These are decisions rendered by arbitrators in an arbitration proceeding, a form of alternative dispute resolution typically chosen by parties in commercial contracts.
- Court Judgments: These are final decisions issued by a court of law after litigation.
Grounds for Enforcement
Enforcement isn’t automatic. The successful party seeking enforcement must demonstrate that the award meets specific criteria. Common grounds for enforcement include:
- Finality of the Award: The award must be final and binding, meaning all avenues for appeal or challenge have been exhausted.
- Recognition of the Award: The jurisdiction where enforcement is sought must recognize the validity of the award, which is often governed by international treaties like the New York Convention.
- Enforceability of the Award: The content of the award must not be contrary to public policy or violate any laws in the jurisdiction where enforcement is sought.
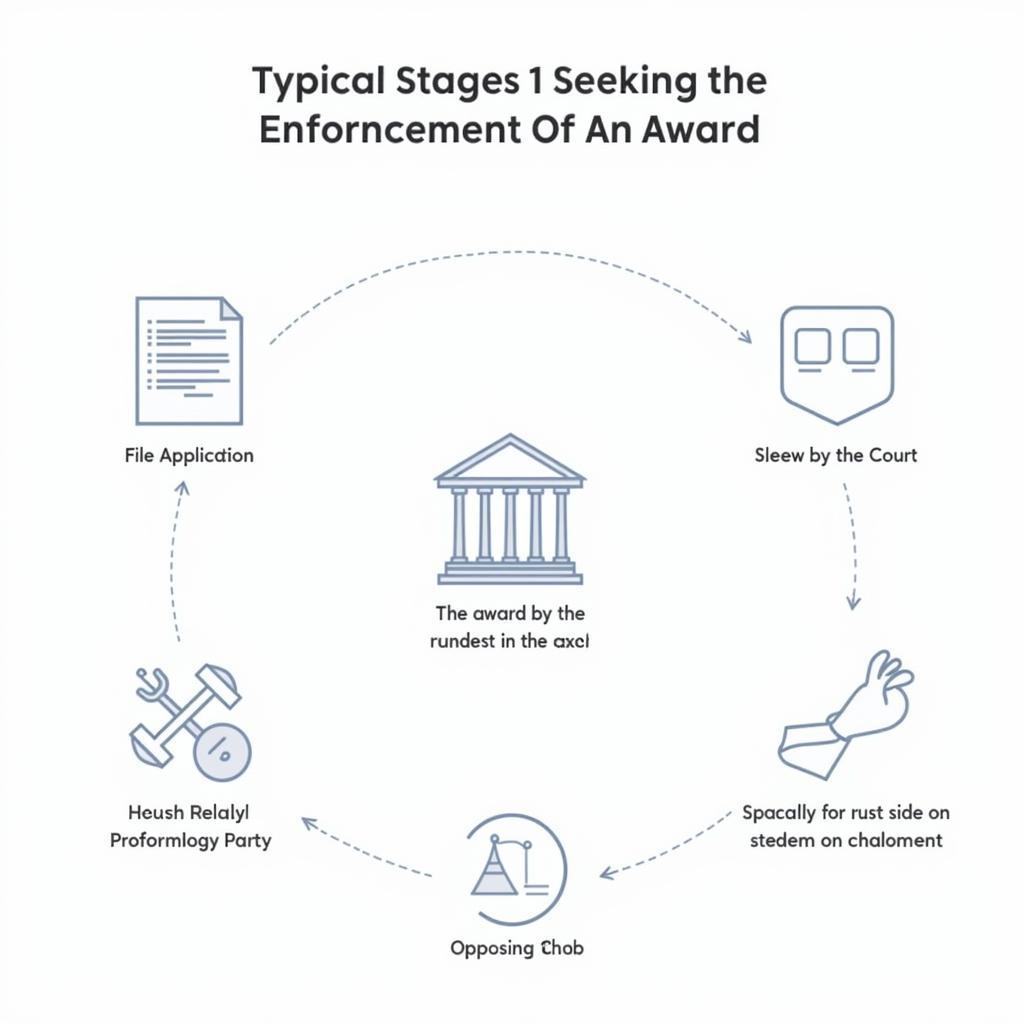 Flowchart illustrating the steps in the enforcement process
Flowchart illustrating the steps in the enforcement process
Steps to File an Application for Enforcement
Navigating the enforcement process requires a meticulous approach and attention to detail. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you file an application for enforcement effectively:
1. Identify the Relevant Jurisdiction: Determining the correct jurisdiction for enforcement is paramount. This is typically the jurisdiction where the losing party’s assets are located or where the enforcement is sought to be carried out.
2. Review the Applicable Laws and Procedures: Each jurisdiction has its own specific laws and regulations governing the enforcement of awards. Consulting with a legal professional specializing in the relevant jurisdiction is crucial to ensure compliance.
3. Prepare the Application for Enforcement: This formal document sets out the basis for the enforcement request. It should clearly identify the parties involved, the nature of the original claim, a copy of the award, and the specific relief sought.
4. File the Application with the Appropriate Court: The application, along with any supporting documents, must be filed with the court designated for enforcement actions in the chosen jurisdiction.
5. Serve the Application on the Losing Party: After filing, the losing party must be officially served with a copy of the application and notified about the enforcement proceedings.
 Image of legal documents being filed with a court clerk
Image of legal documents being filed with a court clerk
6. Attend Court Hearings: The court may schedule hearings to address any objections raised by the losing party or to clarify aspects of the application.
7. Obtain the Enforcement Order: If the court grants the application, it will issue an enforcement order, which is a legally binding document authorizing the seizure of assets or other enforcement measures.
Overcoming Challenges to Enforcement
The enforcement process is not always straightforward. The losing party may raise objections or challenges aimed at delaying or preventing enforcement.
-
Jurisdictional Challenges: The losing party might argue that the chosen court lacks the jurisdiction to hear the enforcement application.
-
Procedural Irregularities: They could allege procedural errors or a lack of due process during the original proceedings that led to the award.
-
Invalidity of the Award: The losing party might attempt to demonstrate that the award is invalid due to bias, fraud, or other grounds.
 A legal team collaborating on an enforcement case strategy
A legal team collaborating on an enforcement case strategy
Seeking Legal Counsel
Navigating the intricacies of filing an application for enforcement of an award demands a comprehensive understanding of complex legal procedures. While this guide provides a general overview, seeking counsel from an experienced attorney specializing in international arbitration or judgment enforcement is essential. They can provide tailored guidance, ensure compliance with all legal requirements, and effectively represent your interests throughout the process.
Conclusion
Enforcing an award is a multifaceted process that requires careful planning, meticulous execution, and a thorough understanding of the applicable legal framework. By following the steps outlined in this guide and seeking expert legal advice, you can significantly enhance your prospects of a successful enforcement action and secure the rightful compensation awarded to you.