The Body’s Defensive Walls: Understanding Leukocyte Barriers
December 29, 2024Leukocyte barriers, the body’s intricate defense systems, are crucial for protecting us from harmful invaders. These complex mechanisms involve various types of white blood cells, also known as leukocytes, working together to identify, neutralize, and eliminate threats. This article will delve into the fascinating world of leukocyte barriers, exploring their different components and how they function to keep us healthy.
The First Line of Defense: Physical and Chemical Barriers
Before leukocytes even come into play, the body has a first line of defense consisting of physical and chemical barriers. These barriers prevent most pathogens from entering in the first place. The skin, for instance, acts as a physical wall, while mucus membranes trap and expel foreign particles. Chemical barriers, such as stomach acid and enzymes in tears and saliva, destroy pathogens before they can cause harm.
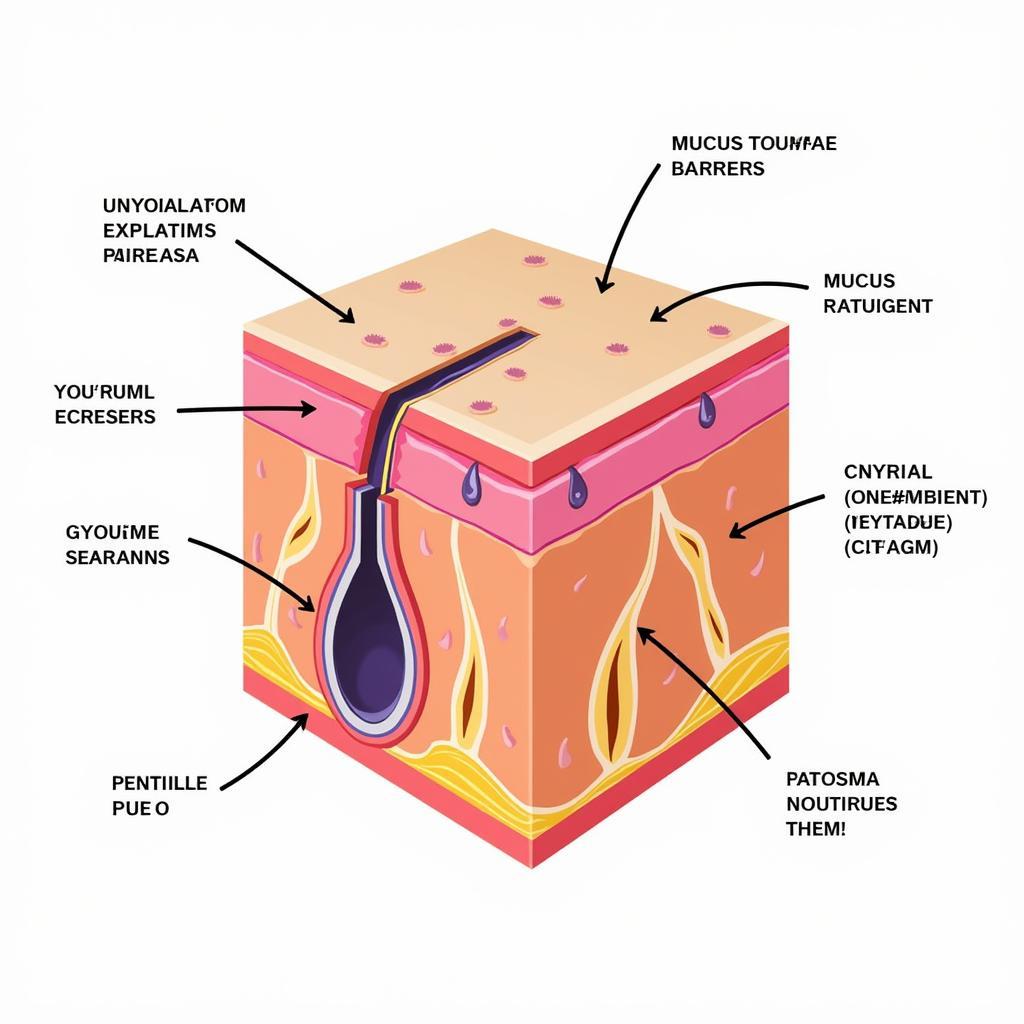 Physical and Chemical Barriers of the Immune System
Physical and Chemical Barriers of the Immune System
The Innate Immune System: Rapid Response Leukocyte Barriers
Once a pathogen breaches the initial barriers, the innate immune system kicks in. This system relies on a variety of leukocytes, including neutrophils, macrophages, and natural killer (NK) cells, to provide a rapid, non-specific response. Neutrophils are the most abundant type of leukocyte and are often the first to arrive at the site of infection, engulfing and destroying pathogens through phagocytosis. Macrophages, another type of phagocytic cell, also play a crucial role in clearing debris and presenting antigens to the adaptive immune system. NK cells, on the other hand, target and eliminate infected or cancerous cells.
The Adaptive Immune System: Specialized Leukocyte Barriers
The adaptive immune system provides a more targeted and long-lasting response to specific pathogens. This system involves two main types of leukocytes: B cells and T cells. B cells produce antibodies, specialized proteins that bind to specific antigens on the surface of pathogens, marking them for destruction. T cells, on the other hand, directly attack infected cells or help coordinate the immune response.
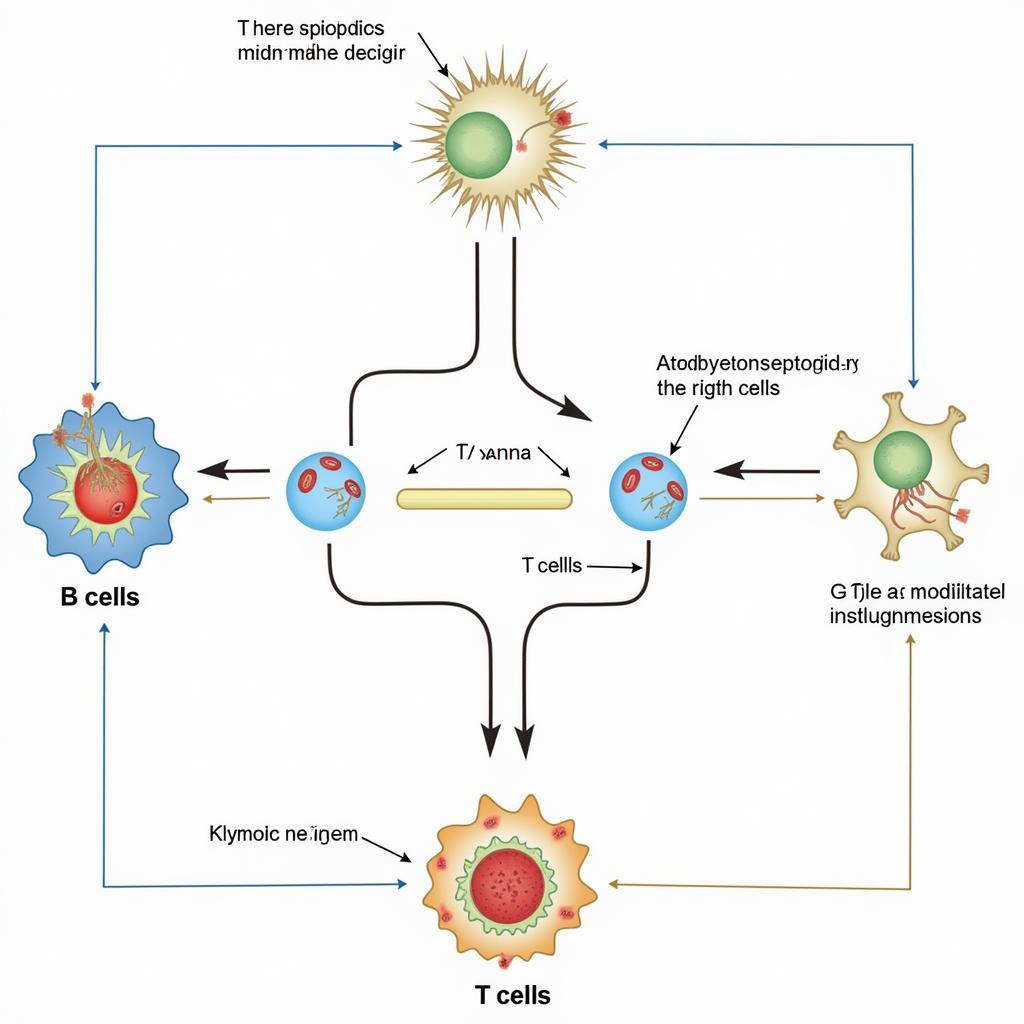 Adaptive Immune Response and Leukocyte Interaction
Adaptive Immune Response and Leukocyte Interaction
How Leukocyte Barriers Work Together: A Coordinated Defense
The innate and adaptive immune systems work together seamlessly to provide comprehensive protection. The innate system provides the initial response, containing the infection and activating the adaptive system. The adaptive system then mounts a targeted attack, eliminating the pathogen and creating immunological memory for future encounters. This coordinated defense is what keeps us healthy in the face of constant exposure to various pathogens.
Maintaining Healthy Leukocyte Barriers: Lifestyle and Diet
Maintaining healthy leukocyte barriers is crucial for overall health and well-being. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients that support immune function. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management also play a vital role in maintaining a robust immune system.
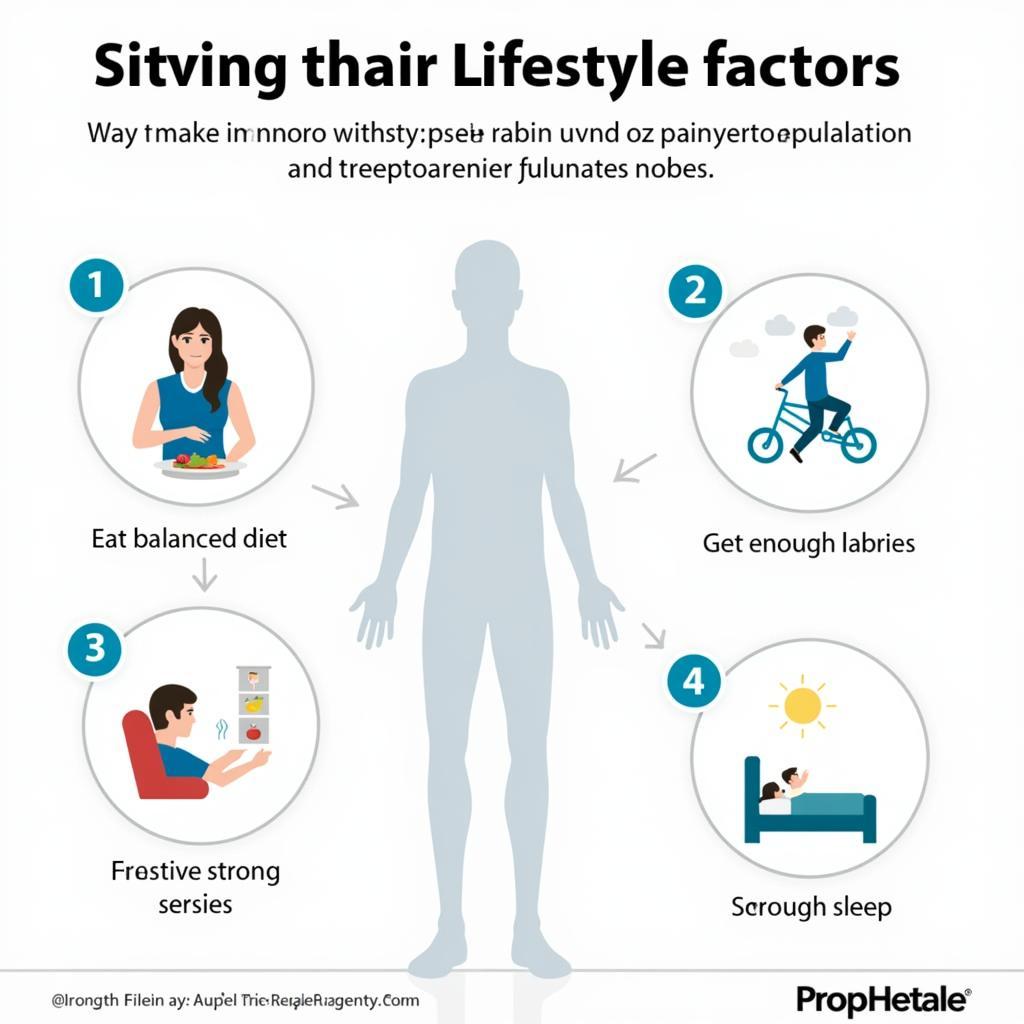 Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle for Strong Immunity
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle for Strong Immunity
In conclusion, leukocyte barriers are essential for protecting us from harmful invaders. Understanding how these complex systems work allows us to appreciate the intricate mechanisms that keep us healthy and take steps to support our immune system. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and understanding the role of leukocyte barriers, we can strengthen our body’s natural defenses and maintain optimal health.
FAQ:
- What are the main types of leukocytes involved in immune responses?
- How do physical and chemical barriers contribute to overall immunity?
- What is the difference between the innate and adaptive immune systems?
- How can I strengthen my leukocyte barriers through lifestyle choices?
- What are some common signs of a weakened immune system?
- What role do antigens play in activating the adaptive immune system?
- How does the body develop immunological memory after an infection?
Need assistance? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 0396443476, Email: [email protected]. Or visit us at: 23 Tháng 3, Đắk Nia, Gia Nghĩa, Đắk Nông, Việt Nam. We have a dedicated customer support team ready to help.