Footballer Suffers On-Field Stroke: Understanding the Risks and Prevention
November 10, 2024A footballer collapsing on the pitch due to a stroke is a chilling scenario, highlighting the unexpected nature of this medical emergency. While often associated with older individuals, strokes can affect athletes, even young and seemingly healthy ones. This article aims to shed light on the factors that contribute to strokes in footballers, the warning signs, and the crucial role of prevention.
Why Might a Footballer Suffer a Stroke?
Several factors can increase the risk of a footballer suffering a stroke. Understanding these is crucial for both players and medical professionals.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Pre-existing conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes significantly increase stroke risk. Regular health screenings are vital for early detection and management of these conditions.
- Head Injuries: Repeated head traumas, common in contact sports like football, can damage blood vessels in the brain, making them more susceptible to clotting and ultimately, stroke.
- Cardiac Issues: Certain heart conditions, such as atrial fibrillation (an irregular heartbeat), can lead to blood clots that travel to the brain and cause a stroke.
- Drug Use: The use of performance-enhancing drugs, including stimulants and some supplements, can raise blood pressure and increase the risk of stroke.
- Genetics: Family history of stroke can also increase an individual’s susceptibility.
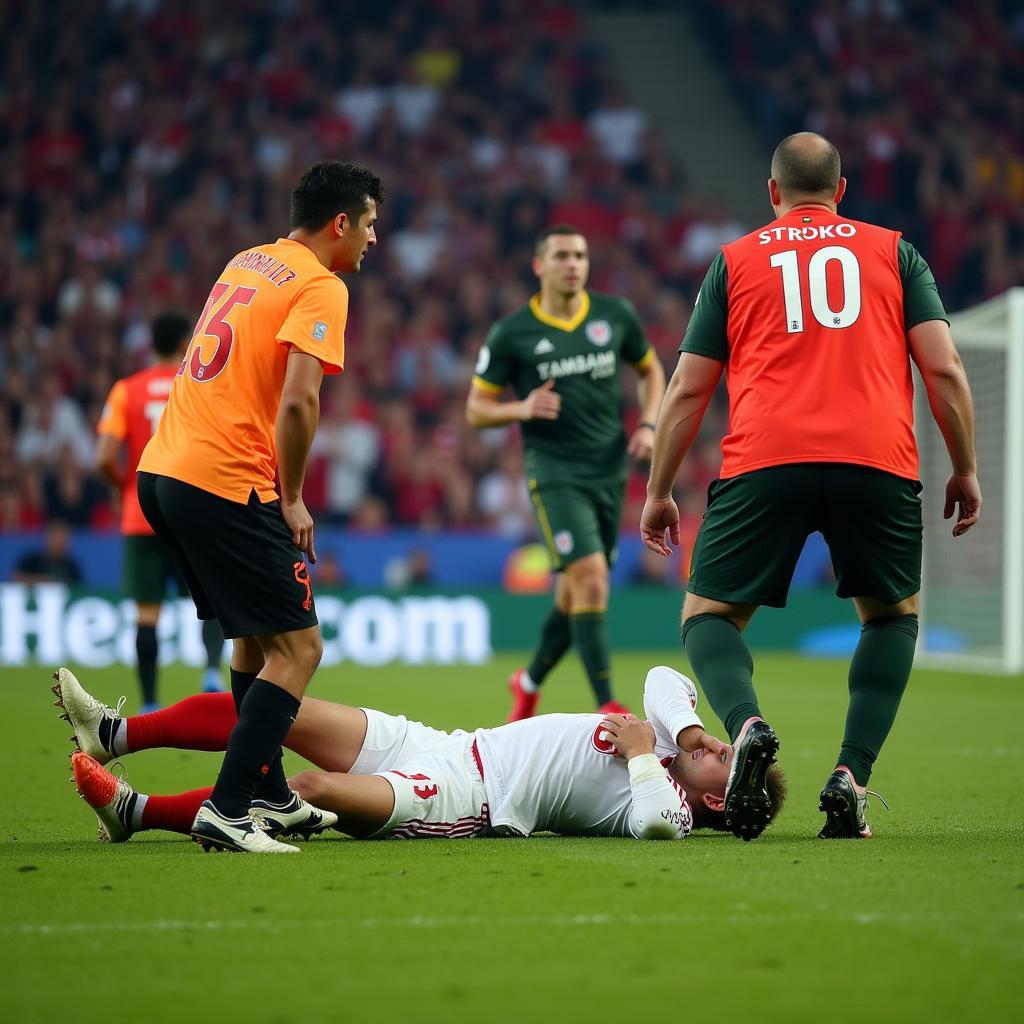 Footballer Collapsing on Pitch Due to Stroke
Footballer Collapsing on Pitch Due to Stroke
Recognizing the Signs of a Stroke: Act FAST
Recognizing the signs of a stroke is paramount for prompt medical intervention. Remember the acronym FAST:
- F (Face Drooping): Is one side of the face numb or drooping? Ask the person to smile.
- A (Arm Weakness): Is one arm weak or numb? Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
- S (Speech Difficulty): Is speech slurred or difficult to understand? Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence.
- T (Time to Call Emergency Services): If any of these signs are present, immediately call emergency medical services.
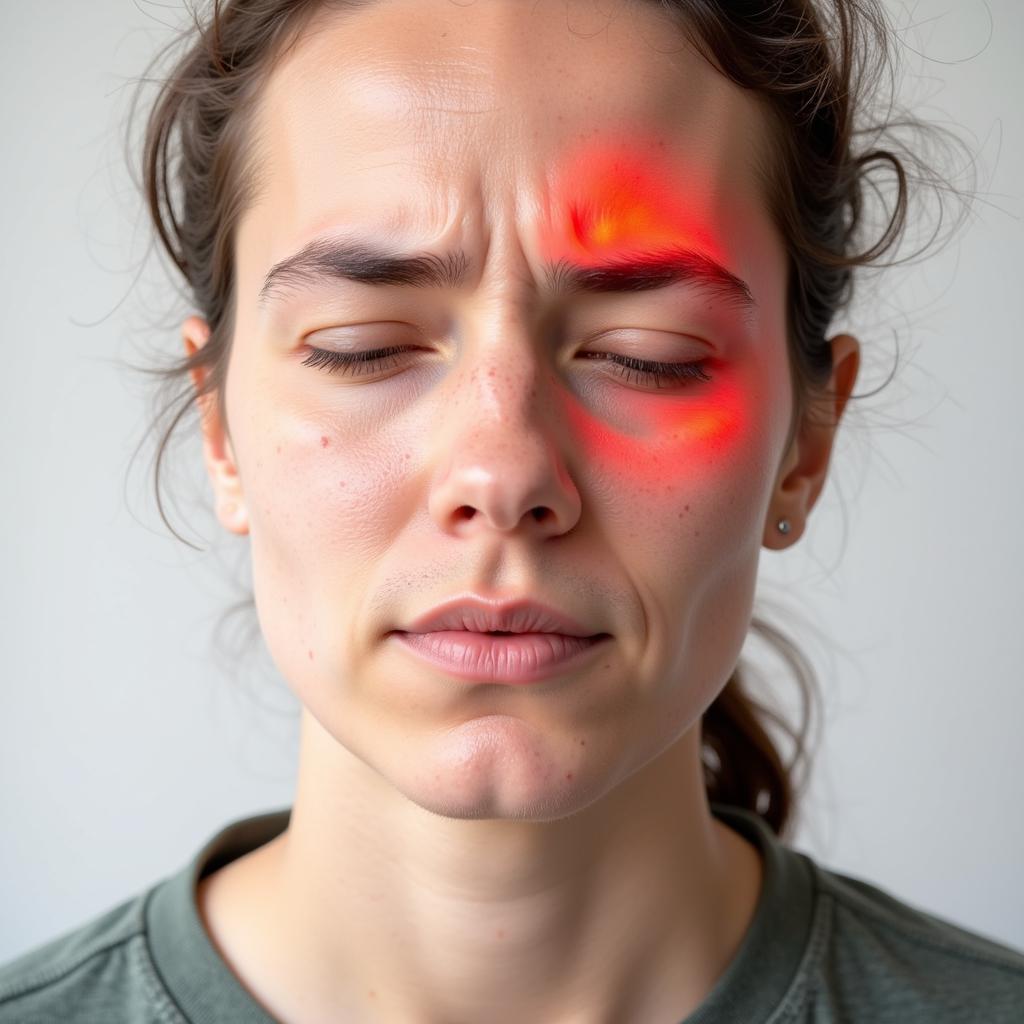 Recognizing Facial Drooping as a Stroke Symptom
Recognizing Facial Drooping as a Stroke Symptom
Preventing Strokes in Footballers: A Proactive Approach
While some risk factors are unavoidable, many can be mitigated through proactive measures.
- Regular Health Checks: Regular medical check-ups are crucial for monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other vital health indicators.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking, significantly reduces stroke risk.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: Effectively managing pre-existing conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes is crucial.
- Head Injury Prevention and Management: Proper protective gear and protocols for managing head injuries are essential in minimizing the risk of stroke.
- Education and Awareness: Educating players, coaches, and medical staff about the signs and symptoms of stroke is crucial for prompt action.
What Happens After a Footballer Suffers a Stroke?
The aftermath of a stroke can vary greatly depending on the severity and the area of the brain affected. Recovery often involves rehabilitation, including physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy. Returning to professional football after a stroke is a challenging journey, and the decision is made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the player’s health and recovery progress.
“The impact of a stroke on an athlete can be devastating, both physically and mentally,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a leading sports physician specializing in neurological conditions. “Early diagnosis and intervention are absolutely crucial for maximizing the chances of a successful recovery.”
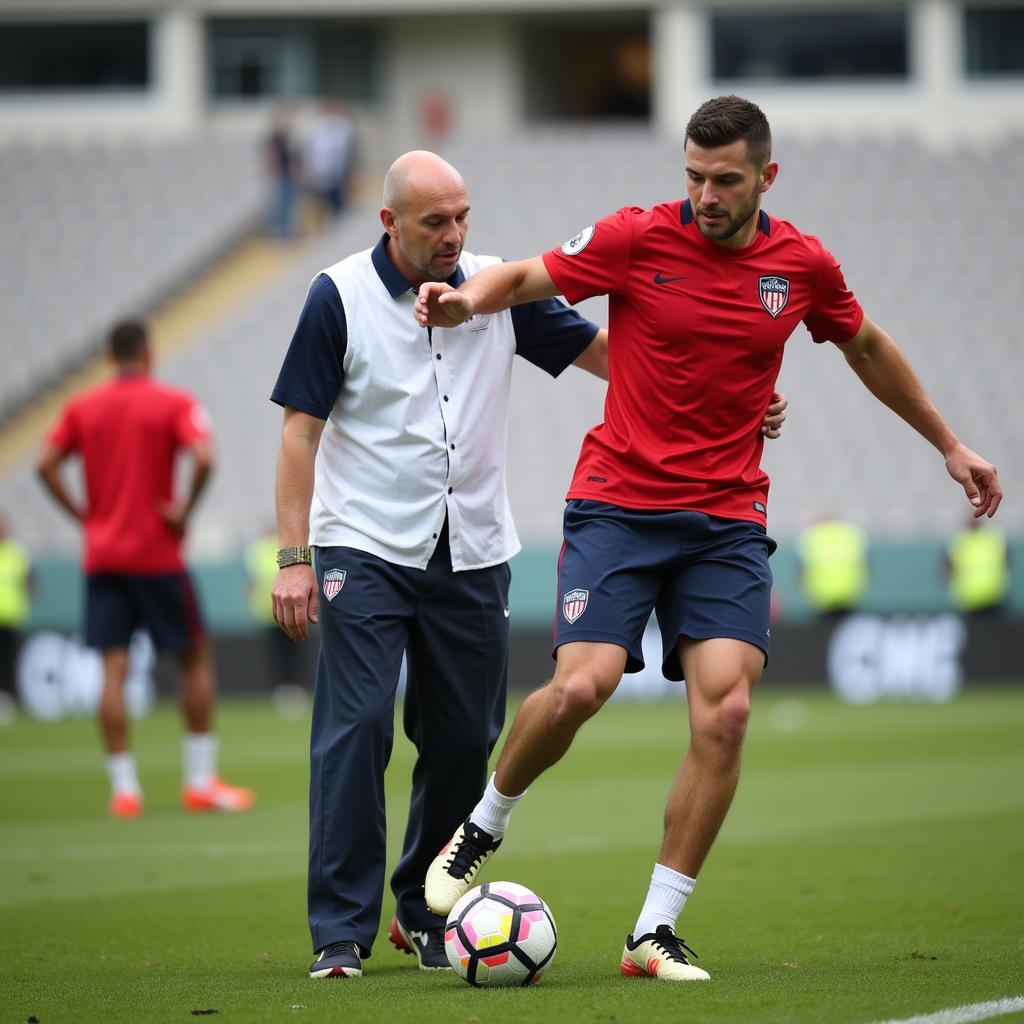 Footballer Undergoing Rehabilitation After Stroke
Footballer Undergoing Rehabilitation After Stroke
Conclusion: Prioritizing Player Health and Well-being
A footballer suffering a stroke on the field is a stark reminder of the importance of prioritizing player health and well-being. By understanding the risks, recognizing the signs, and taking proactive steps towards prevention, we can work towards minimizing the incidence of this potentially life-altering event. Regular health screenings, a healthy lifestyle, and prompt medical attention are key to protecting footballers from the devastating consequences of a stroke.
FAQ
- What are the first signs of a stroke? The first signs can include facial drooping, arm weakness, and speech difficulty.
- Can young athletes have strokes? Yes, although less common, strokes can occur in young athletes due to various factors.
- How can I reduce my risk of stroke? Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying conditions, and regular health checkups are crucial.
- Can a footballer return to play after a stroke? The possibility of returning to play depends on the severity of the stroke and the individual’s recovery.
- What should I do if I suspect someone is having a stroke? Immediately call emergency medical services.
- Are there specific tests to diagnose a stroke? Yes, doctors use imaging tests like CT scans and MRI to diagnose a stroke.
- What is the long-term impact of a stroke? The long-term impact varies greatly depending on the severity and location of the stroke.
Need support? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 0396443476, Email: [email protected], or visit us at 23 Tháng 3, Đắk Nia, Gia Nghĩa, Đắk Nông, Việt Nam.
“Recovery from a stroke requires a multifaceted approach, involving medical professionals, family support, and the athlete’s determination,” adds Dr. David Miller, a renowned neurologist with extensive experience in treating stroke patients. “Every case is unique, and the recovery journey can be long and challenging.”
For more information on health and fitness in football, check out our other articles on [link to related article 1] and [link to related article 2].